Their technique utilizes backscatter analysis to construct “perfectly transmitting” wavefronts.
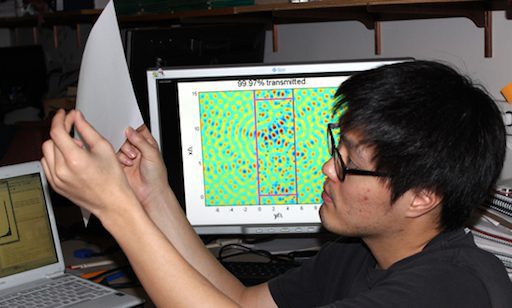

Their technique utilizes backscatter analysis to construct “perfectly transmitting” wavefronts.

Wentzloff aims to remove the necessity of a power outlet or even a battery to power miniature sensors.

The method they developed compares favorably with the best of current techniques, while being faster and easier.

The research group developed special fabrication processes that allows them to stack and bond seven different devices in layers.

By shining the laser on a target and analyzing the reflected light, researchers can tell the chemical composition of the target.
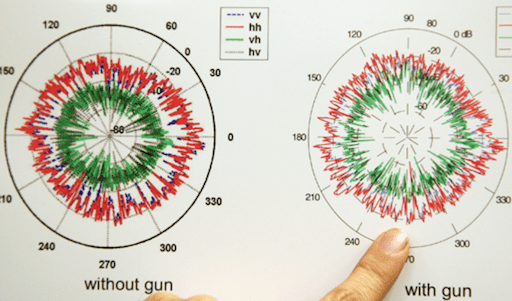
The technology could potentially identify a hidden weapon from a distance in less than a second.

Thanks to HERCULES, scientists are now able to study very dense plasmas — a crucial step in nuclear fusion and astrophysical research.
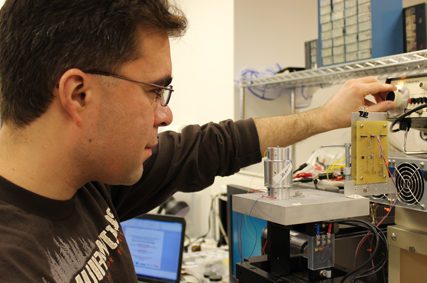
McCullagh is working to develop energy harvesting devices and circuits to power wireless sensor nodes which can monitor bridge health.
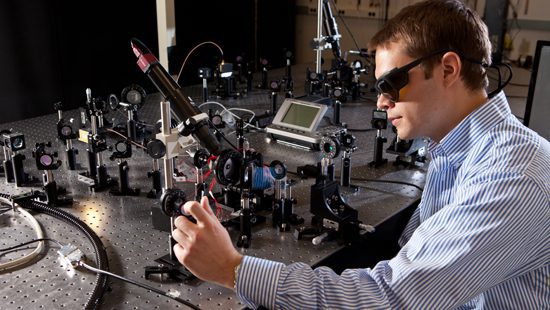
The proposed emitter incorporates plasmonic photoconductors to more efficiently convert power from incident laser light into terahertz radiation.
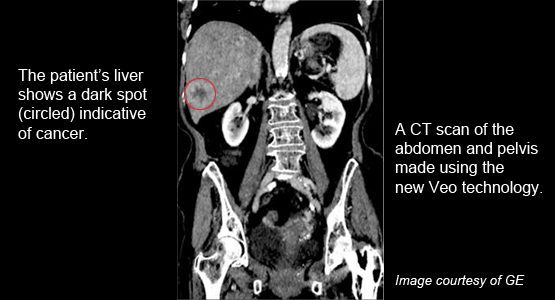
“We’re excited to be adding Veo to the measures we already have in place to ensure that we get diagnostic images using the lowest amount of radiation possible.”